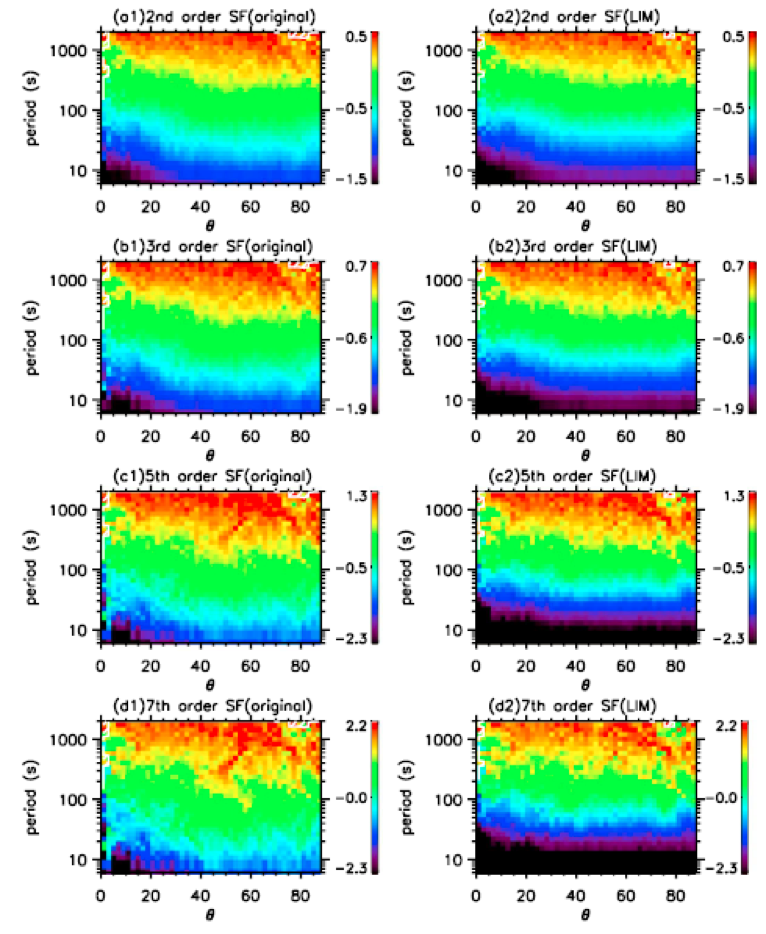
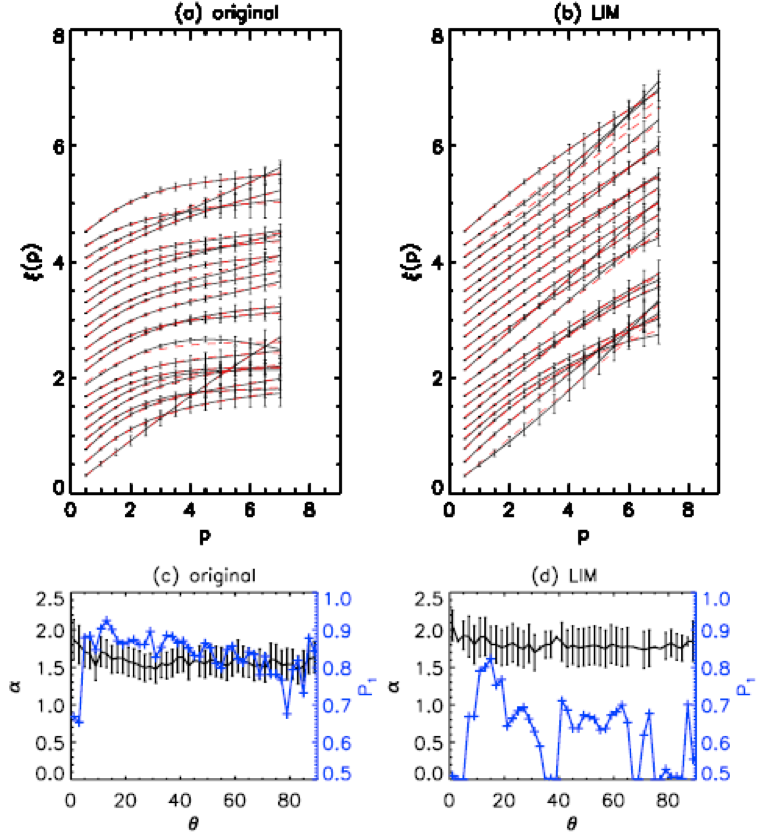
间歇在太阳风湍流中是很重要的结构,并可能与湍流各向异性相关。我们利用局地间歇测量(LIM)方法将磁场数据中的间歇去掉,并按照时间尺度(τ)和径向方向R与局地背景磁场B0的夹角(ΘRB)两个维度分布,计算去除间歇前后的磁场时间序列的结构函数。对不同阶数(p )的结构函数拟合标度律(ξ(p, ΘRB)),发现对于原始时间序列,标度律ξ(p, ΘRB)显示出对角度ΘRB明显的依赖:从ΘRB~0°处的单一分形形态到ΘRB~90°处的多分形形态;但是去掉间歇之后标度律对所有的角度ΘRB都表现出单一分形形态。我们还利用扩展分裂模型来拟合去除间歇前后的结构函数的标度律ξ(p, ΘRB)。扩展分裂模型有两个参数,代指功率谱指数的α以及表明分裂不均等量的P1。在原始的时间序列下,α表现出随角度的变化,从1.9到1.6,而在去掉间歇之后α几乎一直保持在1.8。参数P1在原始的时间序列下随角度从大约0.5提升到0.8,而去掉间歇则在0.5到0.8之间变动。我们最终的结论是:在太阳风湍流中,间歇的各向异性导致了能量谱的各向异性和能量串级的不均等分裂。
该成果发表在Journal of Geophysical Research (JGR): Space Physics 上
文章作者为:裴仲添,何建森,王新,涂传诒,Eckart Marsch,王玲华,闫丽梅
Pei, Z., J. He, X. Wang, C. Tu, E. Marsch, L. Wang, and L. Yan (2016), Influence of intermittency on the anisotropy of magnetic structure functions of solar wind turbulence, J. Geophys. Res. Space Physics, 121, 911–924, doi:10.1002/2015JA021057.
Influence of Intermittency on the Anisotropy of Magnetic Structure Functions of Solar Wind Turbulence
Zhongtian Pei, Jiansen He, Xin Wang, Chuanyi Tu, Eckart Marsch, Linghua Wang, Limei Yan
Intermittency is a significant component of solar wind turbulence, and appears to be connected with the spectral anisotropy of turbulence. We use the Local Intermittency Measure (LIM) to identify and remove intermittency from the magnetic field data measured by the Ulysses spacecraft in fast solar wind. Structure functions are calculated based on the time sequences as obtained before and after removing intermittency, and arranged by time scale (τ) and ΘRB (the angle between local mean magnetic field B0and radial direction R). Thus the scaling exponent (ξ(p, ΘRB)) of every structure function of order (p ) is obtained for different angles. Before removing intermittency, ξ(p, ΘRB) shows a distinctive dependence on ΘRB: from mono-fractal scaling law at ΘRB~0° to multi-fractal scaling law at ΘRB~90°. In contrast after eliminating the intermittency, ξ(p, ΘRB) is found to be more mono-fractal for all ΘRB. The extended structure-function model is applied toξ(p, ΘRB), revealing differences of its fitting parameters α (a proxy of the power spectral index) and P1 (fragmentation fraction) for the cases with and without intermittency. Parameter α shows an evident angular trend and goes from 1.9 down to 1.6 for the case with intermittency, but has a relatively flat profile around 1.8 for the case without intermittency. Parameter P1rises from around 0.5 to above 0.8 with increasing ΘRB for the intermittency case, and is located between 0.5 and 0.8 for the case lacking intermittency. Therefore, we may infer that it is the anisotropy of intermittency which causes the scaling anisotropy of energy spectra and the unequal fragmentation of energy cascading.