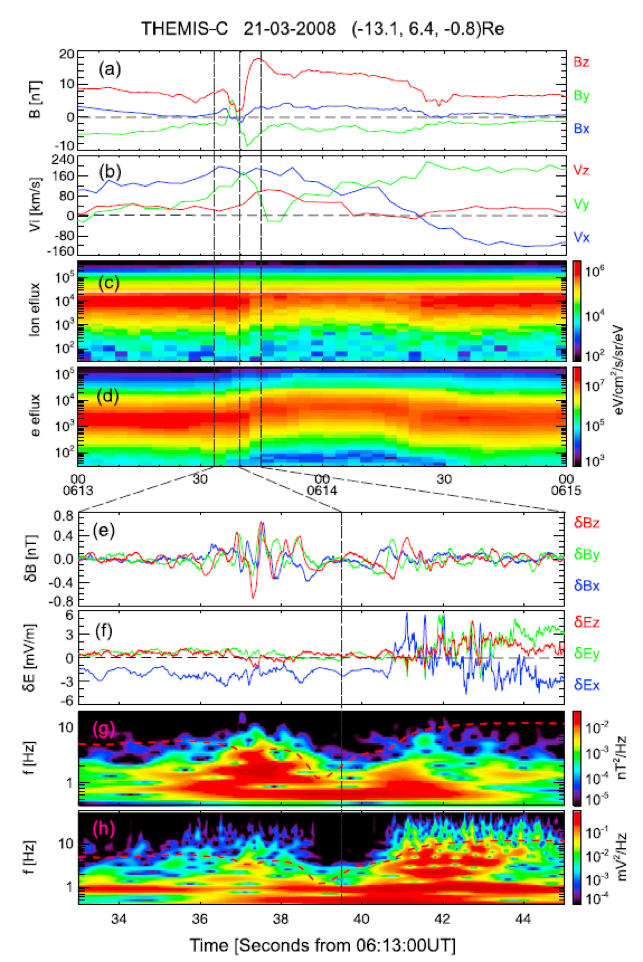
偶极化锋面以北向磁场的陡增为主要特征,是磁尾高速流中经常观察到的离子惯性尺度的磁结构。偶极化锋面伴随着丰富的波动与粒子加速过程,并且对等离子片的动力学过程产生重要影响。本文在偶极化锋面前的磁场降低区域中观察到了电磁波动,这种波动的特征类似于在辐射带中观测到的磁声波。在这一区域我们发现离子的速度分布存在正梯度,这个正梯度能为波动的激发提供自由能。离子分布正梯度的形成可能与磁场降低区中的离子动力学过程有关,被锋面反射并加速的离子叠加在背景离子中可能形成这一分布。该研究有助于进一步了解偶极化锋面相关动动力学过程及其与背景等离子体的相互作用。
该成果近期发表在Geophysical Research Letters (GRL)上,文章链接http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/2016GL068033/full
文章作者:赵多、傅绥燕、孙为杰、G. K. Park、宗秋刚等
Zhao et al., 2016, Geophys. Res. Lett., 43, 3026–3034, doi:10.1002/2016GL068033
Electromagnetic disturbances observed near the dip region ahead of dipolarization front
D. Zhao1, S. Y. Fu1([email protected]), W. J. Sun1, G. K. Parks2, Q. G. Zong1, Q. Q. Shi3, Z. Y. Pu1, Y. B. Cui1, T. Wu1, J. Liu4 and X. Z. Zhou1
1School of Earth and Space Sciences, Peking University, 100871 Beijing, China.
2Space Sciences Laboratory, University of California, Berkeley, California, US.
3School of Space Science and Physics, Shandong University at Weihai, Weihai, China.
4Department of Earth, Planetary, and Space Sciences, University of California, Los Angeles, California, USA
Dipolarization front (DF) is a thin magnetic structure embedded in fast flows in the magnetotail, which plays an important role in particle acceleration, flow braking, wave excitation, and other related processes. Electromagnetic disturbances near the magnetic dip region in front of DFs are investigated using Time History of Events and Macroscale Interactions during Substorms probe observations in this paper. Strong magnetic field and electric field fluctuations, with several wave bands below and around the lower hybrid frequency, are found in an event on 21 March 2008. The properties of the wave are similar to that of magnetosonic wave. Detailed analyses show that the phase space density for ions in the perpendicular direction has a positive slope near the local Alfvén speed, which is a possible free-energy source for the generation of the wave. This type of ion distribution could result from the earthward reflected ions ahead of DF, though other forming mechanism could not be fully ruled out.